Incomplete Multi-view Clustering
A Method for Consensus Anchor Graph Learning for Incomplete Multi-View Clustering
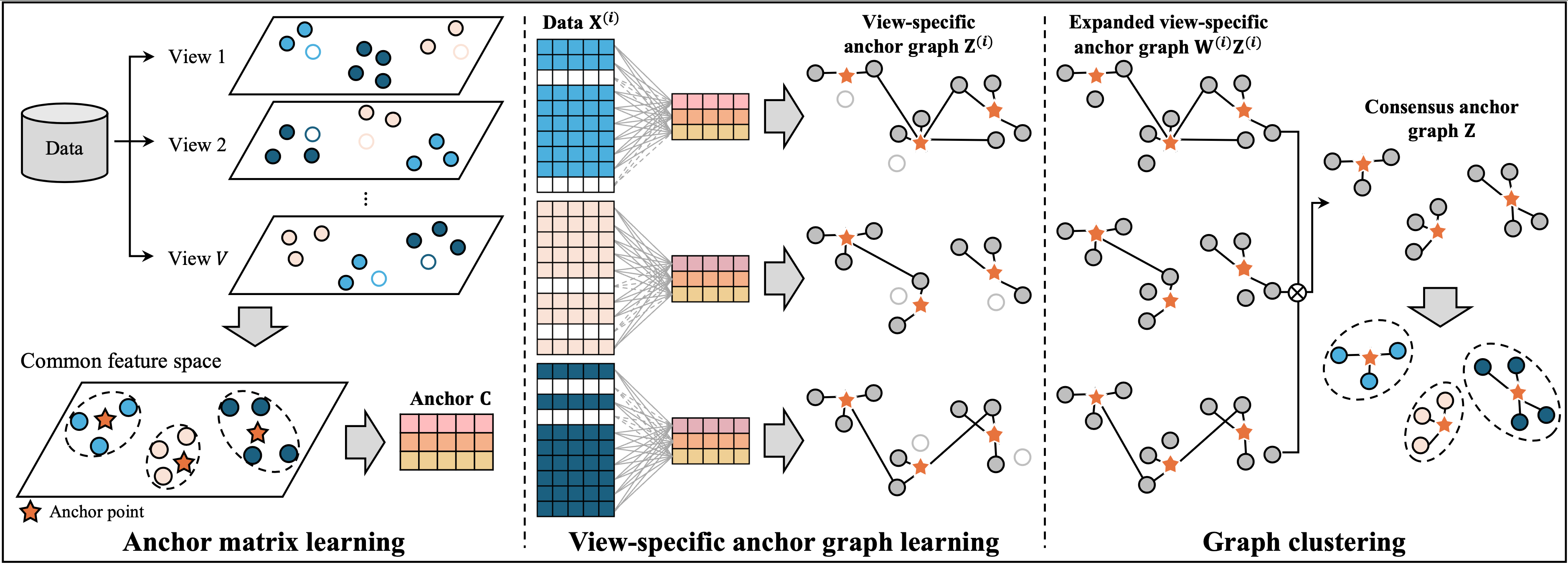
Multi-view clustering (MVC) is a prevalent method for integrating heterogeneous domain-specific information from diverse views. However, most MVC methods assume that all views have complete observed data, which is often unfeasible in practical applications due to missing or corrupted data. To address this limitation, incomplete multi-view clustering (IMC) was developed to handle partially observed data. Recently, anchor graph-based IMC has been proposed, as conventional IMC methods typically involve quadratic or higher complexity, which substantially restricts their scalability to large and complex datasets. Although these methods enhance efficiency by approximating sample–anchor relationships, their performance still degrades under conditions of high missing rates. Therefore, we propose a scalable anchor graph-based IMC algorithm specifically designed for large-scale datasets. Our method enhances clustering performance in severely incomplete data by combining two strategies. First, a bipartite anchor learning strategy minimizes computational cost to nearly linear time while preserving inter-view structure. Second, a consensus graph learning term integrates view-specific discriminability with cross-view consistency. Dynamic anchor updates enable the framework to effectively adapt to varying dataset scales and missing patterns. The framework’s effectiveness was confirmed via experiments on 16 datasets across multiple domains, where we evaluated its clustering accuracy and execution time. The proposed method’s validity is verified by its ability to outperform representative IMC baselines and scales to large datasets. Its reliability is also maintained even with high incompleteness levels, highlighting its practicality for large-scale, real-world applications.